
ブログ
 TensorFlow vs PyTorch vs Neural Designer
TensorFlow vs PyTorch vs Neural Designer
 現在人気の機械学習プラットホームである
TensorFlow,
PyTorch,
Neural Designer
は、それぞれGoogle、Facebook、Artelnicsによって開発されました。
これらのフレームワークはすべてニューラルネットワークをベースにしていますが、機能、使いやすさ、
パフォーマンスなどの面でいくつかの重要な違いがあります。
ここでは以下に示すように、Levenberg-Marquardtアルゴリズムを用いた場合、Neural DesignerはTensorFlowよりも1.91倍、
Adamを用いたPyTorchよりも1.21倍高い精度で学習できます。
さらに、Neural DesignerはTensorFlowの5.71倍、PyTorchの8.21倍の速さでこのニューラルネットワークを学習します。
現在人気の機械学習プラットホームである
TensorFlow,
PyTorch,
Neural Designer
は、それぞれGoogle、Facebook、Artelnicsによって開発されました。
これらのフレームワークはすべてニューラルネットワークをベースにしていますが、機能、使いやすさ、
パフォーマンスなどの面でいくつかの重要な違いがあります。
ここでは以下に示すように、Levenberg-Marquardtアルゴリズムを用いた場合、Neural DesignerはTensorFlowよりも1.91倍、
Adamを用いたPyTorchよりも1.21倍高い精度で学習できます。
さらに、Neural DesignerはTensorFlowの5.71倍、PyTorchの8.21倍の速さでこのニューラルネットワークを学習します。
リンク:
 はじめに
はじめに
機械学習プラットフォームで最も重要な要素の一つは、その学習精度です。
この記事では、ベンチマークアプリケーションに対するTensorFlow、PyTorch、Neural Designerの学習精度を測定し、
それらのプラットフォームで得られる学習速度を比較する事を目的とします。
トレーニング精度の最も重要な要因は、使用される最適化アルゴリズムです。 TensorFlowとPyTorchはC++とPythonでプログラムされているのに対し、Neural DesignerはすべてC++で プログラムされています。
トレーニング精度の最も重要な要因は、使用される最適化アルゴリズムです。 TensorFlowとPyTorchはC++とPythonでプログラムされているのに対し、Neural DesignerはすべてC++で プログラムされています。

 ベンチマーク問題
ベンチマーク問題
最初のステップでは、各機械学習プラットフォームの性能について結論を出すのに十分な、一般的なベンチマークアプリケーションを選択します。
ここでは入力-目標サンプルのセットを近似するニューラルネットワークを訓練します。
近似アプリケーションは、データセット、ニューラルネットワーク、および関連する学習戦略によって、以下のように定義します。
 データセット
データセット
 ニューラルネットワーク
ニューラルネットワーク
 トレーニング戦略
トレーニング戦略
 データセット
データセット- ベンチマーク: Rosenbrock
- 入力数: 10
- 目標数: 1
- サンプル数: 10000
- ファイルサイズ: 2.38 MB (download)
 ニューラルネットワーク
ニューラルネットワーク- Layer数: 2
- Layer 1:
- -タイプ: パーセプトロン (全結合)
- -入力数: 10
- -ニューロン数: 10
- -活性化関数: Hyperbolic tangent (tanh)
- Layer 2:
- -タイプ: パーセプトロン (全結合)
- -入力数: 10
- -ニューロン数: 1
- -活性化関数: Linear
- 初期化: 一様でランダム[-1,1]
 トレーニング戦略
トレーニング戦略- 損失関数:
- -Error: 平均二乗誤差 (MSE)
- -正則化: なし
- 最適化アルゴリズム (TensorFlow、PyTorch):
- -アルゴリズム: Adaptive Moment Estimation (Adam)
- -バッチサイズ: 1000
- -最大エポック数: 10000
- 最適化アルゴリズム(Neural Designer):
- -アルゴリズム: Levenberg-Marquardt (LM)
- -最大エポック数: 1000
 計算リソース、及びコード
計算リソース、及びコード
ここでは、以下のスペックのコンピュータを用いて比較します。
各フレームワークは、TensorFlow (2.1.0), PyTorch (1.7.0), Neural Designer (5.9.0)をインストールします。
以下のコードは、TensorFlow、Pytorchによる実装例です。
PyTorchでこのアプリケーションを構築するには、いくつかのPythonスクリプトも必要です。 また、こちらからもコードをダウンロードできます。
TensorFlow、PyTorch、Neural Designerでそれぞれ実装できたら実行します。
OS
Windows10CPU
CPU Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8259CL CPU @ 2.50GHz物理RAM
16.0GB各フレームワークは、TensorFlow (2.1.0), PyTorch (1.7.0), Neural Designer (5.9.0)をインストールします。
以下のコードは、TensorFlow、Pytorchによる実装例です。
TensorFlow
#TENSORFLOW CODE import tensorflow as tf import pandas as pd import time import numpy as np #read data float32 start_time = time.time() filename = "C:/R_new.csv" df_test = pd.read_csv(filename, nrows=100) float_cols = [c for c in df_test if df_test[c].dtype == "float64"] float32_cols = {c: np.float32 for c in float_cols} data = pd.read_csv(filename, engine='c', dtype=float32_cols) print("Loading time: ", round(time.time() - start_time), " seconds") x = data.iloc[:,:-1].values y = data.iloc[:,[-1]].values initializer = tf.keras.initializers.RandomUniform(minval=-1., maxval=1.) #build model model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([tf.keras.layers.Dense(1000, activation = 'tanh', kernel_initializer = initializer, bias_initializer=initializer), tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation = 'linear', kernel_initializer = initializer, bias_initializer=initializer)]) #compile model model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss = 'mean_squared_error') #train model start_time = time.time() history = model.fit(x, y, batch_size = 1000, epochs = 1000) print("Training time: ", round(time.time() - start_time), " seconds")
PyTorchでこのアプリケーションを構築するには、いくつかのPythonスクリプトも必要です。 また、こちらからもコードをダウンロードできます。
PyTorch
#PYTORCH CODE import pandas as pd import time import torch import numpy as np import statistics def init_weights(m): if type(m) == torch.nn.Linear: torch.nn.init.uniform_(m.weight, a=-1.0, b=1.0) torch.nn.init.uniform_(m.bias.data, a=-1.0, b=1.0) epoch = 1000 total_samples, batch_size, input_variables, hidden_neurons, output_variables = 1000000, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1 device = torch.device("cuda:0") # read data float32 start_time = time.time() filename = "C:/R_new.csv" df_test = pd.read_csv(filename, nrows=100) float_cols = [c for c in df_test if df_test[c].dtype == "float64"] float32_cols = {c: np.float32 for c in float_cols} dataset = pd.read_csv(filename, engine='c', dtype=float32_cols) print("Loading time: ", round(time.time() - start_time), " seconds") x = torch.tensor(dataset.iloc[:,:-1].values, dtype = torch.float32) y = torch.tensor(dataset.iloc[:,[-1]].values, dtype = torch.float32) # build model model = torch.nn.Sequential(torch.nn.Linear(input_variables, hidden_neurons), torch.nn.Tanh(), torch.nn.Linear(hidden_neurons, output_variables)).cuda() # initialize weights model.apply(init_weights) # compile model learning_rate = 0.001 loss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction = 'mean') optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) indices = np.arange(0,total_samples) start = time.time() for j in range(epoch): mse=[] t0 = time.time() for i in range(0, total_samples, batch_size): batch_indices = indices[i:i+batch_size] batch_x, batch_y = x[batch_indices], y[batch_indices] batch_x = batch_x.cuda() batch_y = batch_y.cuda() outputs = model.forward(batch_x) loss = loss_fn(outputs, batch_y) model.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() mse.append(loss.item()) print("Epoch:", j+1,"/1000", "[================================] - ","loss: ", statistics.mean(mse)) t1 = time.time() - t0 print("Elapsed time: ", int(round(t1 )), "sec") end = time.time() elapsed = end - start print("Training time: ",int(round(elapsed )), "seconds")
TensorFlow、PyTorch、Neural Designerでそれぞれ実装できたら実行します。
 計算結果
計算結果
前述のコードを用いて実行した各プラットホームが提供する訓練時間の結果を比較します。
まず、TensowFlowの結果を示します。
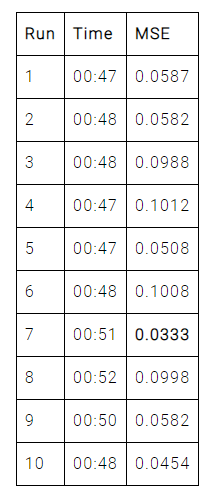
これを見ると、TensorFlowによる最小平均二乗誤差は0.0333、 10回の実行での平均二乗誤差の平均は0.0705となります。また、平均学習時間は48.6秒となりました。
次にPyTorchの結果を示します。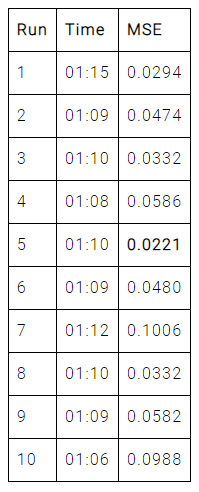
PyTorchによる結果では、10回の実行でPyTorchの最小平均二乗誤差は0.0221、平均二乗誤差の平均は0.0529です。 また、平均学習時間は69.8秒となりました。
最後に、Neural Designerによる結果は以下のようになります。
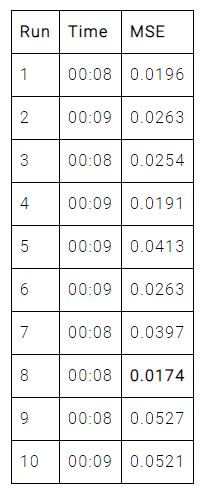
Neural Designerでは、最小の平均二乗誤差は0.0174、10回の実行での平均二乗誤差の平均は0.0320となりました。 平均学習時間は8.5秒です。
次の表は各機械学習プラットホームの結果をまとめたものです。
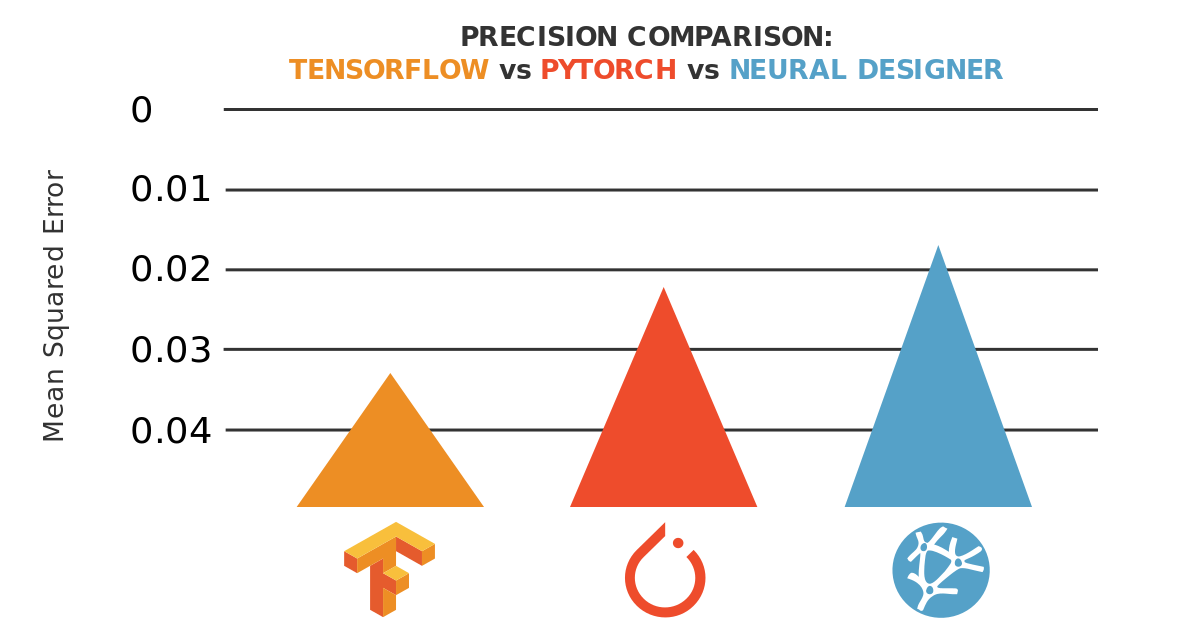
最後に、今回のケースでのTensorFlow、PyTorch、Neural Designerの学習精度をグラフ化したのが以下の図です。 LMアルゴリズムを使用したNeural Designerの最小平均二乗誤差と平均二乗誤差は、Adamを使用したTensorFlowとPyTorchよりも
小さくなっていることがわかります。
これらの指標を用いると、今回のベンチマークにおけるNeural Designerの精度は、TensorFlowの1.91倍、PyTorchの1.27倍であると言えます。
学習時間については、今回のベンチマークでは、Neural DesignerはTensorFlowの約5.72倍、PyTorchの約8.21倍の速さで学習を行っています。
LMアルゴリズムを使用したNeural Designerの最小平均二乗誤差と平均二乗誤差は、Adamを使用したTensorFlowとPyTorchよりも
小さくなっていることがわかります。
これらの指標を用いると、今回のベンチマークにおけるNeural Designerの精度は、TensorFlowの1.91倍、PyTorchの1.27倍であると言えます。
学習時間については、今回のベンチマークでは、Neural DesignerはTensorFlowの約5.72倍、PyTorchの約8.21倍の速さで学習を行っています。
まず、TensowFlowの結果を示します。
TensowFlow

これを見ると、TensorFlowによる最小平均二乗誤差は0.0333、 10回の実行での平均二乗誤差の平均は0.0705となります。また、平均学習時間は48.6秒となりました。
次にPyTorchの結果を示します。
PyTorch

PyTorchによる結果では、10回の実行でPyTorchの最小平均二乗誤差は0.0221、平均二乗誤差の平均は0.0529です。 また、平均学習時間は69.8秒となりました。
最後に、Neural Designerによる結果は以下のようになります。
Neural Designer

Neural Designerでは、最小の平均二乗誤差は0.0174、10回の実行での平均二乗誤差の平均は0.0320となりました。 平均学習時間は8.5秒です。
次の表は各機械学習プラットホームの結果をまとめたものです。
| TensorFlow | PyTorch | Neural Designer | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum MSE | 0.0333 | 0.0221 | 0.0174 |
| Average MSE | 0.0705 | 0.0529 | 0.0320 |
| Average training time | 48.6 seconds | 69.8 seconds | 8.5 seconds |
最後に、今回のケースでのTensorFlow、PyTorch、Neural Designerの学習精度をグラフ化したのが以下の図です。
 LMアルゴリズムを使用したNeural Designerの最小平均二乗誤差と平均二乗誤差は、Adamを使用したTensorFlowとPyTorchよりも
小さくなっていることがわかります。
これらの指標を用いると、今回のベンチマークにおけるNeural Designerの精度は、TensorFlowの1.91倍、PyTorchの1.27倍であると言えます。
学習時間については、今回のベンチマークでは、Neural DesignerはTensorFlowの約5.72倍、PyTorchの約8.21倍の速さで学習を行っています。
LMアルゴリズムを使用したNeural Designerの最小平均二乗誤差と平均二乗誤差は、Adamを使用したTensorFlowとPyTorchよりも
小さくなっていることがわかります。
これらの指標を用いると、今回のベンチマークにおけるNeural Designerの精度は、TensorFlowの1.91倍、PyTorchの1.27倍であると言えます。
学習時間については、今回のベンチマークでは、Neural DesignerはTensorFlowの約5.72倍、PyTorchの約8.21倍の速さで学習を行っています。
 まとめ
まとめ
Neural Designerには、準ニュートン法やLevenberg-Marquardtアルゴリズムなどの2次最適化アルゴリズムが実装されています。
これらのアルゴリズムは、中小規模のデータセットに対して、Adamなどの1次活性化関数よりも優れた収束特性を持っています。
今回の記事で紹介したベンチマークでは、Neural Designerの精度はTensorFlowのx1.91倍、PyTorchのx1.27倍という結果を得ました。 この結果を再現するには、Neural Designerの フリートライアルをダウンロードして、本記事で紹介した手順に従ってください。
今回の記事で紹介したベンチマークでは、Neural Designerの精度はTensorFlowのx1.91倍、PyTorchのx1.27倍という結果を得ました。 この結果を再現するには、Neural Designerの フリートライアルをダウンロードして、本記事で紹介した手順に従ってください。
